















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
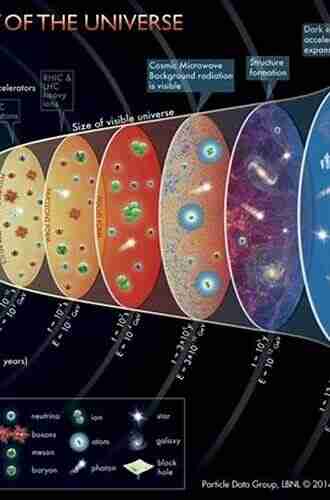
An Investigation Of The History Of Matter From The Big Bang To The Present

Have you ever wondered how everything around us came into existence? How did the vast universe, with its billions of galaxies, stars, and planets, start? These questions have intrigued scientists and philosophers for centuries, leading to a never-ending quest to understand the history of matter. From the explosive beginning of the universe, known as the Big Bang, to the diverse and complex world we live in today, this article will take you on a fascinating journey through time and space.
The Big Bang: The Birth of our Universe
The story of matter begins around 13.8 billion years ago with an event known as the Big Bang. This primeval explosion marked the beginning of time, space, and matter itself. At this moment, the universe was incredibly hot and dense, with all the matter and energy concentrated into a tiny point. Then, in a fraction of a second, the universe rapidly expanded, cooled down, and began to form the building blocks of matter.
During the first few minutes after the Big Bang, protons, neutrons, and electrons started to come together to form the simplest element, hydrogen. As the universe continued to expand and cool, the first stars began to ignite, triggering the fusion of hydrogen into more complex elements such as helium and lithium. These reactions inside the cores of stars produced the heavier elements that would later become vital for the formation of planets and even life.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 39013 KB |
| Print length | : | 496 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Hardcover | : | 192 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 15.8 ounces |
| Dimensions | : | 6.14 x 0.5 x 9.21 inches |
Formation of Stars, Galaxies, and Elements
Over billions of years, gravity played a crucial role in shaping the universe. The first stars formed when extremely dense clouds of gas collapsed under their own gravity. These early stars were massive and short-lived, burning out quickly and releasing their enriched matter into the surrounding space.
As time passed, galaxies started to form, with each containing billions or even trillions of stars. These galaxies acted as cosmic factories, continuously producing new stars and more complex elements. Through processes like supernovae, where massive stars explode at the end of their lives, elements such as carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen were scattered throughout space, enriching the raw materials available for future star and planet formation.
In the midst of this cosmic symphony, smaller objects like planets and moons started to take shape around newly forming stars. These celestial bodies were born from the leftover materials of their parent star's formation, carrying within them the same elements that were created and distributed over billions of years.
Our Solar System and the Formation of Earth
About 4.6 billion years ago, within one of the many galaxies in the universe, our own solar system began to form. A cloud of gas and dust that originated from a previous supernova explosion started to collapse under its own gravity. As the cloud continued to contract, it formed a swirling disk known as the protoplanetary disk.
Within this disk, particles started to collide and stick together, gradually growing in size. Over millions of years, these small building blocks, called planetesimals, merged to form larger objects known as protoplanets. Within our protoplanetary disk, one of these protoplanets would eventually become our home, Earth.
At this stage, the early Earth was a hostile place. Frequent asteroid impacts, volcanic activity, and a toxic atmosphere made it inhospitable for life as we know it. However, over time, the surface of our planet cooled down, allowing the formation of oceans and the emergence of the first life forms.
Life on Earth: From Microorganisms to Complex Organisms
The origin of life on Earth remains one of the greatest mysteries in scientific history. Although the exact processes that led to the formation of the first living organisms are still unknown, scientists believe that early Earth provided the necessary conditions for life to emerge.
It is thought that the first life forms were single-celled microorganisms, such as bacteria. These simple organisms thrived in the oceans, taking advantage of the abundant nutrients and energy sources. Over millions of years, these microorganisms evolved and diversified, giving rise to more complex life forms like plants, animals, and eventually, humans.
The evolution of life on Earth was driven by a combination of genetic mutations, natural selection, and environmental changes. Gradually, species became more complex, developing specialized organs, intricate nervous systems, and the ability to adapt to different environments.
The Present and Beyond: Exploring the Cosmos and Unraveling the Mysteries of Matter
Today, humanity stands at the cutting edge of scientific exploration, with a wealth of knowledge about the history of matter. Through advancements in technology, we have been able to study the universe in unprecedented detail, unraveling its mysteries one by one.
Scientists continue to study the origins of matter through experiments conducted in powerful particle accelerators, such as the Large Hadron Collider. These experiments allow us to recreate the conditions that existed moments after the Big Bang, helping us understand the fundamental forces and particles that make up our universe.
Beyond our own solar system, astronomers explore distant galaxies and search for planets that may harbor life. Through the study of exoplanets, planets outside our solar system, scientists hope to gain insights into the conditions necessary for life to exist elsewhere in the universe.
: A Never-Ending Journey of Discovery
The investigation into the history of matter, from the Big Bang to the present, is a captivating and ongoing scientific endeavor. It reveals the incredible journey that has led to the formation of our universe, the birth and evolution of stars and galaxies, the creation of elements, the emergence of life on Earth, and the continuous exploration of the cosmos.
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of the universe, new questions arise, and humanity's curiosity remains unquenched. The history of matter is an enthralling story that reminds us of our place in the vastness of space and time, inspiring us to push the boundaries of knowledge and seek answers to our most profound questions about existence itself.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 39013 KB |
| Print length | : | 496 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Hardcover | : | 192 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 15.8 ounces |
| Dimensions | : | 6.14 x 0.5 x 9.21 inches |
This book investigates the question of how matter has evolved since its origin in the Big Bang, from the cosmological synthesis of hydrogen and helium to the generation of the complex set of nuclei that comprise our world and our selves. A central theme is the evolution of gravitationally contained thermonuclear reactors, otherwise known as stars. Our current understanding is presented systematically and quantitatively, by combining simple analytic models with new state-of-the-art computer simulations.
The narrative begins with the clues (primarily the solar system abundance pattern),the constraining physics (primarily nuclear and particle physics),and the thermonuclear burning in the Big Bang itself. It continues with a step-by-step description of how stars evolve by nuclear reactions, a critical investigation of supernova explosion mechanisms and the formation of neutron stars and of black holes, and an analysis of how such explosions appear to astronomers (illustrated by comparison with recent observations). It concludes with a synthesis of these ideas for galactic evolution, with implications for nucleosynthesis in the first generation of stars and for the solar system abundance pattern. Emphasis is given to questions that remain open, and to active research areas that bridge the disciplines of astronomy, cosmochemistry, physics, and planetary and space science. Extensive references are given.

 Fernando Pessoa
Fernando PessoaThe Ultimate Guide to New Addition Subtraction Games...
In this day and age, countless parents are...

 Ethan Mitchell
Ethan MitchellThe Ultimate Guide for the Aspiring Pianist: Unleash Your...
Are you a beginner pianist feeling...

 Gerald Parker
Gerald ParkerWow Robot Club Janice Gunstone - The Mastermind Behind...
Robots have always fascinated...

 Dylan Hayes
Dylan HayesIdeal For Catching Up At Home: CGP KS2 Geography
Are you looking for the perfect resource to...

 Kevin Turner
Kevin TurnerThe Ultimate Pictorial Travel Guide To Vietnam: Explore...
Discover the rich...

 D'Angelo Carter
D'Angelo CarterUnlocking the Secrets of Compact Stars: Exploring...
Compact stars have...

 Isaiah Price
Isaiah PriceUnveiling the Hidden Gem: Google Places Goliath Valley...
Are you tired of visiting the same old...

 Donald Ward
Donald WardEssays Towards Theory Of Knowledge: Exploring the Depths...
Are you ready to delve into...

 Thomas Mann
Thomas MannThe Ultimate PMP Project Management Professional All In...
Are you ready to take your project...

 Trevor Bell
Trevor Bell10 Incredible Stories From Life In Football That Will...
The Beautiful Game - Football...

 Zachary Cox
Zachary Cox100 Amazing And Unexpected Uses For Coconut Oil
Coconut oil, a versatile and widely loved...

 Owen Simmons
Owen SimmonsUnveiling the Enigma of Die Blaue Brosche: A Family’s...
Have you ever heard of Die Blaue Brosche...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Jedidiah HayesKs3 Biology Study Question Higher: Boost Your Knowledge with Engaging and...
Jedidiah HayesKs3 Biology Study Question Higher: Boost Your Knowledge with Engaging and...
 James HayesUnveiling the Multifaceted World of Introductory Combinatorics: Exploring the...
James HayesUnveiling the Multifaceted World of Introductory Combinatorics: Exploring the... John SteinbeckFollow ·11.2k
John SteinbeckFollow ·11.2k Ismael HayesFollow ·5.9k
Ismael HayesFollow ·5.9k Howard BlairFollow ·6.4k
Howard BlairFollow ·6.4k Todd TurnerFollow ·6.6k
Todd TurnerFollow ·6.6k Juan RulfoFollow ·6k
Juan RulfoFollow ·6k Finn CoxFollow ·5.3k
Finn CoxFollow ·5.3k Roald DahlFollow ·6.1k
Roald DahlFollow ·6.1k Robert Louis StevensonFollow ·4.6k
Robert Louis StevensonFollow ·4.6k